Advanced DNA-for CCGS
Extraneous Informational Websites-All Free
ISOGG.org http://www.isogg.org/
International Society of Genetic Genealogy is a non-commercial non-profit organization with over 8,000 members in over 75 countries. There are no dues or fees to join. It is entirely self-supporting by its members. One donates time to giving presentations or hosting workshops at local genealogical societies, or creating photocopies to promote the society at a convention.
ISOGG Wiki http://www.isogg.org/wiki/Wiki_Welcome_Page
A free genetic genealogy encyclopedia established for the benefit and education of the genetic genealogy community. It currently has 356 articles about all DNA tests, projects, project administration, haplogroups and other genetic resources
Extraneous Testing Websites-All Free-Be Sure To Use Them
Y-Search.org http://www.ysearch.org/
Anyone who tested Y-DNA with any testing company may submit their allele results and be compared with anyone else in the same database. The database gives matches with genetic differences and email
Mito-Search.org http://www.mitosearch.org/
Anyone who tested MtDNA with any testing company may submit their mutation results and be compared with anyone else in the same database
Gedmatch.com http://v2.gedmatch.com/select.php
Anyone who has tested their Autosomal and Y-DNA through an Illumina testing lab may upload their raw data to this website and have their data compared to all others in the database. Ancestry.Com, 23 and Me and Family Tree DNA all qualify.
Gedmatch.com is owned and run by two men with a science background but no corporate backing. In fact, they have day jobs. Recently, a couple of their servers failed and they are working to get back online.
Currently, they have comparative analyzing raw DNA data for people who previously were uploaded in their database. The filters currently online are:
• “One to Many” Matches
• “One to One” Matches
• “X-One to One” Matches
• “Gedcom to DNA” Matches
• “Search All Gedcoms”
Previously, prior to the server problems Gedmatch had the filters named above but also had filters showing matches on chromosome images and several ethnicity filters showing one’s deep ancestry in graphs, circles and other formats.
Once Gedmatch is again up and running it is expected they will once again allow people to upload their raw data and gedcoms.
Advanced Search-FTDNA
Utilizing the above search tool, simply by checking any of the boxes, one can find their Y-DNA, mt-DNA, Family Finder (autosomal DNA) and X-Chromosome matches in the entire FTDNA database or in any project in which you are a member. Caviat: If you did not take a specific test, you will not have matches in that test.
Discovering your Y-DNA Relatives:
1) You must have the same haplotype
Haplogroups/Haplotypes and their Origins
A haplogroup is a genetic population group of people who share a common ancestor on the patrilineal or matrilineal line. Haplogroups are assigned letters of the alphabet, and refinements consist of additional number and letter combinations.
1) As a prerequisite to comparing two people in Y-DNA or mt-DNA tests, both must have the same haplogroup. With Autosomal testing each party can have differing haplogroup.
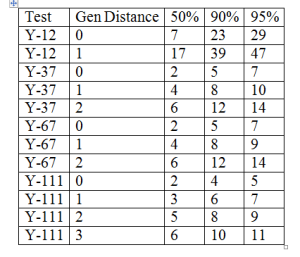
2) Then you need your genetic distance. This is given to you on your Personal Page.There is a genetic distance for each Y-DNA test-12, 25, 37, 67, 111.
A genetic distance of “0” is exact and the closest relationship possible.
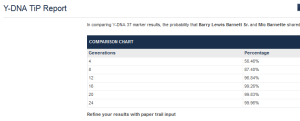
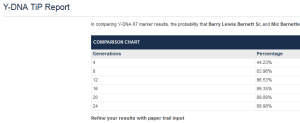
Y-DNA Genetic Distance
Probability that your common ancestor lived no longer than this number of generations ago.
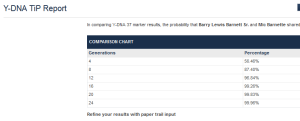
Family Tree DNA Time Predictor (FTDNATiP TM)
Family Tree DNA Time Predictor (FTDNATiP TM) is a program used to calculate estimates of Time to Most Recent Common Ancestor (TMRCA). It is the world’s first calculator that incorporates mutation rates specific to each marker. This increases the power and precision of estimates. Used to compare yourself with one of your Y-DNA matches
Mt-DNA Matching
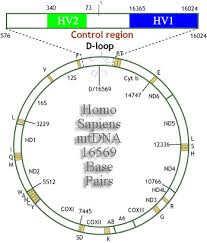
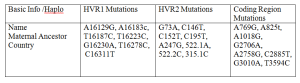
Mt-DNA HVR-1, HVR-2 and Coding Regions
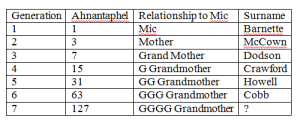
mt-DNA Match Generational and Relationship Chart
Autosomal DNA (Family Finder)
Recombination
Recombination is the mixing of the DNA on each chromosome one receives from one’s mother and father. Different chromosomes and different parts of each chromosome are more or less likely to recombine in a single generation.
Random-ness
Random – Definition and More from the Free Merriam-Webster …
www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/random
without definite aim, direction, rule, or method <subjects chosen at random
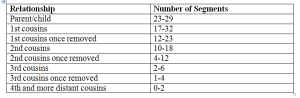
Identical By Descent (IBD)
IBD stands for Identical By Descent. This means the DNA matches because it comes from a common ancestor. IBD can refer to a single mutation or to a segment of DNA. If a mutation or segment of DNA is IBD among a group of people, it comes from a common ancestor.
The Family Finder relationship predictions require a minimum number of results in a row to be identical in order to identify that the segment is likely to be IBD.
Identical By State (IBS)
IBS stands for Identical By State,
meaning the DNA matches by coincidence. When two individuals share numerous individual results without being related, those results are IBS. This happens often in closed societies where inhabitants live near one another over numerous generations and family members of that society frequently intermarry among one another.
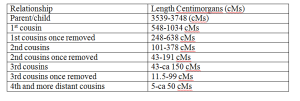
Ranges of total centimorgans of IBD segments expected, based on family relationship
Ranges of the number of shared IBD segments based on family relationship
Steps to Performing Triangulaton/In Common With Filters with Using the Matrix Tool, Chromosome Browser and Excel CVS Features
Step 1: Choose a base person
Step 2: Click on In Common With/Trianulation Symbol
This will give you numerous other people who match both you and the base person you chose
This means both you and your base person are related to those whose name came up in your results. You and your base person may or may not relate to your results people the same way or even on the same side of the family. It just means you both are related to the results person.
Step 3: Make a list of your “In Common With” matches
Using Matrix Tool
Step 1: Choose the names from the list you made in Step 4.
Move the names from the list on the Left to the space on the Right. There is a limited number of spaces in the Matrix Tool. If there are many names, you may have to run the names more than once.
Step 2: In your lower screen you will see the Matrix Tool.
It will indicate those from above who are related and those who are not. Make a list of those related to your Base person.
Using the Chromosome Browser
Step 1: Go to the Chromosome Browser.
Choose up to 5 names (the maximum allowed. If there are more than 5 names you will have to repeat this procedure after completing it a first time).
You will see the 5 names at the top of the page. Each person will have a different color icon.
Run the comparison.
Step 2: Color coded segments will appear on one or more chromosome images.
The colors refer back to each person in the comparison list at the top of the page.
The colored lines represent the lengths of segments shared between you and that color coded person.
The colored line chromosome icon is the chromosome you and the results person share with the largest segment. 5+/- cMs is the default. The defaut can be adjusted up to 10cM and as low as 1 cM. When this adjustment is made, the sements on the chromosome images, likewise, will change.
Create a CVS/Excel spreadsheet
Step 1: Click on the CVS link near Chromosome Browser. This will load data into an Excel spreadsheet. The data represents the chromosome number and length of each segment you and the results person share.
Step 2: Give the Excel spreadsheet a name.
Step 3: If necessary, clear the Chromosome Browser and return to the list of matches and repeat steps 1 through 3 until you have worked with each results person.
Each time you download information from the Chromosome Browser, cut and paste the new information from a new excel spreadsheet into your first (named) spreadsheet.
Step 4: Now, SORT your data.
Click on the Sort Function. In your first field, sort by “Chromosome”. In the second field, sort by “Starting Location”.
Step 5: Once your list is in chronological order by Chromosome you can look at the starting point for each person on each chromosome.
You can color code matching start-end entries. This indicates where a match on a specific chromosome is located. I use Excel 2007 and it will not save the color coding. To compensate, I place spaces between matches to preserve and show the results.
Step 6: Using the theory of Tiangulation…what you have done is mark the “in common with” areas of your base person and the results person. You will need to figure out what family the location belongs to by working with your Base person and Results person.
Step 7: Since the Results person matches both you and your Base person, the match you have in common is on the same side of the family as the Base person. For instance the base person relates to you on your maternal side, that is the side your Results person also relates to you.
Uploading Your Gedcom (FTDNA)
To upload your file:
1. First, you must export your GEDCOM file from the software in which you developed
2. your family tree (you should be able to do this by clicking on File in that program
3. Then Export to save this file to your computer).
4. Log into your myFTDNA account. (https://www.familytreedna.com/login.aspx)
5. On the top menu bar, find the My Account menu.
6. From the My Account menu, select GEDCOM/Family Tree.
7. On the My Account – GEDCOM/Family Tree page, look for the GEDCOM section and
8. Click on the Next button to start the GEDCOM Upload wizard.
Uploading Your Gedcom (23 and Me)
1. Go to Friends and Family
2. Go to Build and Share Your Family Tree
3. Click on “Actions”- Upload Gecom
4. Follow instructions
YOUR ETHNICITY
FROM THE ISOGG WIKI:
Overall accuracy and sophistication of the biogeographical ancestry analysis rated on a 1-10 scale with 10 being excellent and 1 being poor:
23 and Me: Overall rating: 7
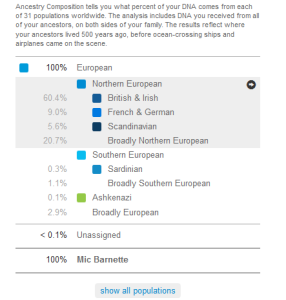
The Ancestry Composition feature offers a map view which displays one’s ancestral components from various regions of the world as of 500 years ago, a split view for those who also have one or both parents who have been tested by 23andMe, and a breakdown by chromosone.
Three settings are available: conservative, standard, and speculative. Overall accuracy is reasonably good, but predictions in Europe are still not optimal, particularly in the speculative mode. Ancestry Finder provides a breakdown of one’s ancestry by country.
Family Tree DNA: Overall rating: 3.5
The MyOrigins analysis is much improved over FTDNA’s previous Population Finder analysis. However, it still lacks specificity, particularly for Europe. No chromosome painting feature is available.
Ancestry.Com: Overall rating: 3
The Genetic Ethnicity Summary consistently overestimates the Central European and Scandinavian ancestral components for people whose ancestors were from the British Isles. The ancestral component from the British Isles is overestimated for people whose ancestors were from continental Europe. Overall, the European ancestry predictions tend to be inaccurate.
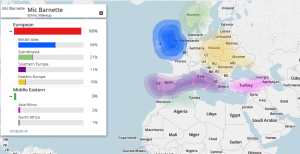
23 and Me Ancestry Composition: Map and Ethnicity Chart
FTDNA-My Origins
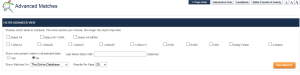
Discovering X-Chromosome Matches
23 and Me:
You will have to compare each of your matches. The X-chromosome will show in the 23rd chromosome location in the Chromosome Browser. Matches can be visually compared in the Browser and start-end data printed out.
Family Finder:
In the Advanced Matches search tool, click on X-Chromosome.
X-Chromsomes also show in the Chromosome Browser. This data is included on CSV Excel spreadsheets and can be printed out.
Gedmatch.com
X-Chromosome matches show in the Matches List. X-Chromosome matches can be compared with an X-Chromosome tool.
Learn About X-Chromosomes and Matching
Go To a website called micsxchromosome at http://micsxchromosome.micbarnette.com and visit the post Finding X-Chromosomes
Or just go to http://micsxchromosome.micbarnette.com/x-chromosomes/




Leave a Reply